Total
Laparoscopic Gastropexy
A Modern Solution for GDV Prevention: Dedicated to veterinary laparoscopic gastropexy, an innovative surgical technique designed to combat gastric dilatation-volvulus (GDV).
What Is Total Laparoscopic Gastropexy?
Laparoscopic gastropexy is a surgical procedure commonly performed in veterinary medicine to prevent gastric dilatation-volvulus (GDV), also known as gastric torsion or bloat, in dogs. GDV is a life-threatening condition where the stomach twists and distends, potentially leading to obstruction of blood flow, tissue necrosis, shock, and death if not promptly treated.
Why is Laparoscopic Gastropexy Important?
Certain dog breeds are more prone to GDV, including large and deep-chested breeds like Great Danes, German Shepherds, and Boxers. GDV can occur suddenly, often with no warning, and requires emergency surgery. A gastropexy greatly reduces the risk of this condition and is often performed as a preventive measure in at-risk dogs.
Gastopexy is recommended during other routine procedures, such as spaying or neutering, for convenience and reduced anaesthetic exposure.
Gastropexy Procedure
Laparoscopic gastropexy is a surgical procedure performed on pets, primarily dogs, to prevent gastric dilatation-volvulus (GDV), commonly known as bloat.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the surgery, we will conduct a thorough preoperative evaluation, which may include physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies (such as X-rays or ultrasound) to assess the patient’s overall health and confirm the diagnosis of GDV or assess the risk of developing it.
Anaesthesia
The pet is placed under general anaesthesia to ensure they remain unconscious and pain-free throughout the procedure. An intravenous catheter is usually placed to administer fluids and medications during the surgery. Anaesthesia and vital signs, such as heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure, are closely monitored throughout the procedure.
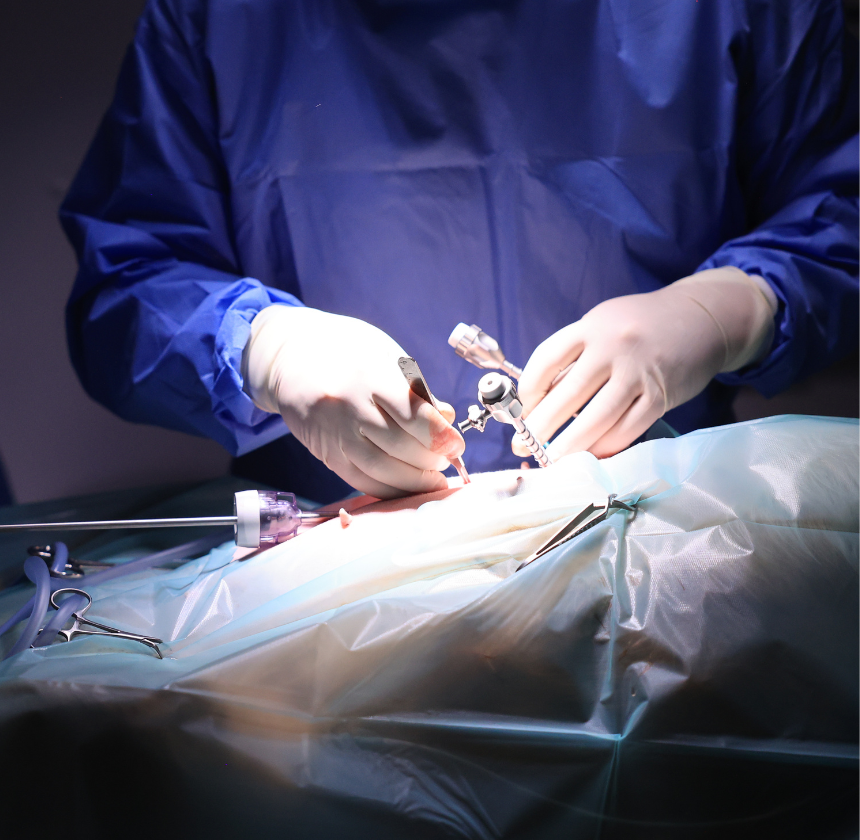
Surgical Incisions
Small incisions are made in the abdominal wall, allowing specialised instruments and a laparoscopic camera to be inserted, typically using three ports for the camera and instruments.
Visualisation
A laparoscope, a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and light source, is inserted through one of the trocars. The laparoscope lets us visualise the abdominal organs on a monitor, including the stomach, liver, spleen, and intestines.
The surgeon carefully identifies the stomach and determines the optimal attachment site on the abdominal wall or diaphragm.
Gastropexy
This involves attaching the stomach to the abdominal wall or diaphragm using sutures, staples, or tissue anchors. The goal is to create a permanent adhesion that prevents the stomach from rotating or twisting in the future.
Closure & Recovery
Once the gastropexy is completed, the laparoscopic instruments are removed, and the surgical incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue. The pet is carefully monitored during the recovery period in the hospital until fully awake from anaesthesia. Pain management medications may be provided to ensure comfort during the recovery process.
Gastropexy Benefits in Pets
Overall, veterinary laparoscopic gastropexy offers a safe, effective, and minimally invasive approach to preventing GDV in dogs, providing numerous benefits. It represents a valuable option for dog owners seeking to proactively safeguard their pets against this life-threatening condition.
Prevents GDV
Gastropexy secures the stomach to the abdominal wall, significantly reducing the risk of life-threatening GDV, where the stomach twists and cuts off blood supply.
Proactive Care
Ideal for at-risk breeds like Great Danes, German Shepherds, and Boxers, gastropexy provides peace of mind for owners of predisposed dogs.
Minimally Invasive
When performed laparoscopically, the procedure involves smaller incisions, resulting in reduced pain, faster recovery, and less scarring.
Life Saving Measure
Without gastropexy, GDV can develop suddenly and requires emergency surgery, which carries higher risks and costs.
Convenient Timing
It can often be performed alongside other routine surgeries like spaying or neutering, reducing the need for multiple anaesthesia events.
Improves Quality of Life
By preventing a critical condition, gastropexy ensures your pet can enjoy a healthier, longer life.