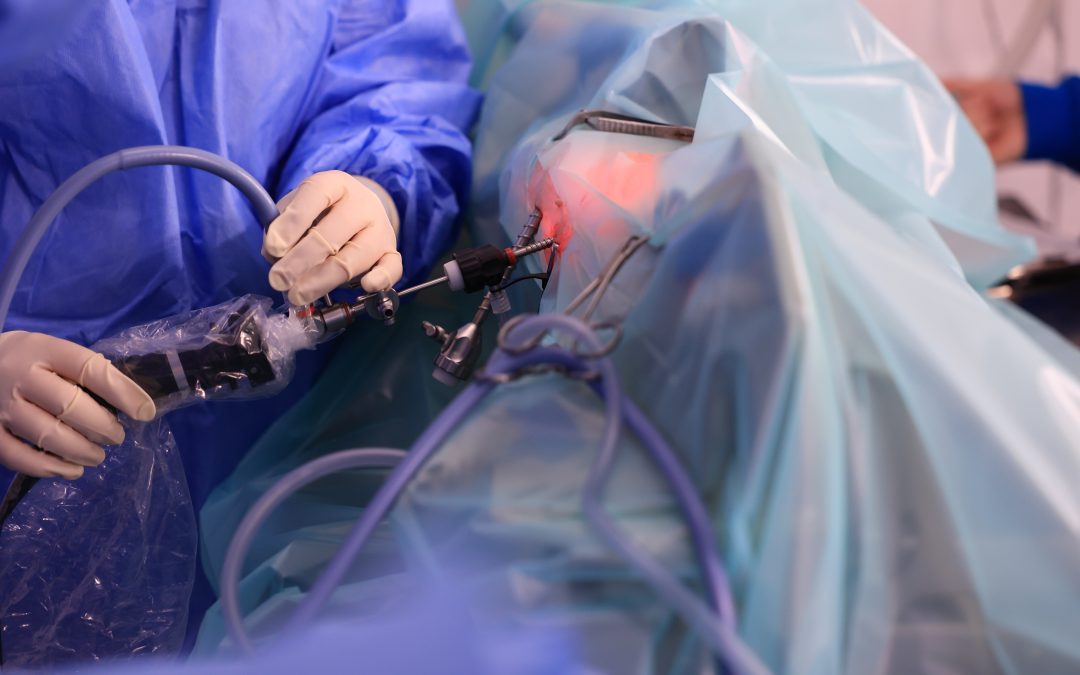
Laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical technique, has transformed veterinary medicine and made a significant impact on the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions and surgical procedures in our beloved animal companions.
The Beginning of Laparoscopy:
Laparoscopy was initially created for use in human medicine and human surgical procedures. However, in the early 1900s, George Kelling began practicing laparoscopic procedures on canine patients using a cystoscope to explore the abdominal cavity, though this was not the beginning of laparoscopy in veterinary medicine. In 1910, Hans Christian Jacobaeus and George Kelling advanced these practices into human medicine, where they have continued to develop, with the vast majority of surgical procedures now being carried out laparoscopically, including appendectomies and cholecystectomies. Officially, laparoscopy in veterinary medicine can be traced back to the mid-20th century. Veterinary surgeons (VS) saw the potential benefits of using laparoscopy for their furry patients. The first documented use of laparoscopy in veterinary procedures occurred in the 1970s, beginning its journey into the veterinary world.
Advancements In Technology:
As technology advanced, so did the capabilities of laparoscopic equipment. The 1980s witnessed the development of smaller, more specialised instruments, making it easier for VSs to perform more intricate procedures. The introduction of high-resolution cameras further improved visualisation, enabling VSs to explore the abdominal cavity with greater clarity, thus improving surgical success and minimising surgical complications. The introduction of using carbon dioxide to expand the abdominal cavity also made a breakthrough, as previously, nitrous oxide was used – even in patients who were not anaesthetised!
Application In Small Animal Medicine:
Laparoscopy quickly gained popularity in small animal medicine due to its minimally invasive nature. Procedures such as spaying, biopsies, gastropexies and exploratory surgeries became more efficient and less traumatic for patients. The reduced recovery time and postoperative discomfort had a strong impact on how VSs performed these routine surgeries and further increased its popularity.
Take over into Large Animal Surgery:
While initially more common in small animal medicine, laparoscopy gradually made its way into large animal medicine. VSs embraced this technique for procedures like ovariectomy in mares and standing laparoscopic techniques in cattle. The benefits of reduced postoperative complications and shorter recovery times were evident across all species.
Challenges and Innovations:
Despite its numerous advantages, laparoscopic procedures faced challenges such as limited instrument size and cost. However, ongoing innovations addressed these concerns, with the development of specialised tools and training programs to ensure widespread adoption. These advancements expanded the range of laparoscopic applications in veterinary practice.
Present Day:
Laparoscopy is now an integral part of veterinary surgery. From routine procedures to complex surgeries, veterinary surgeons rely on this technique to provide optimal care for their patients. The continuous evolution of laparoscopic technology ensures that veterinary medicine remains at the forefront of minimally invasive surgical practices and continues to follow suit of those used in human medicine.