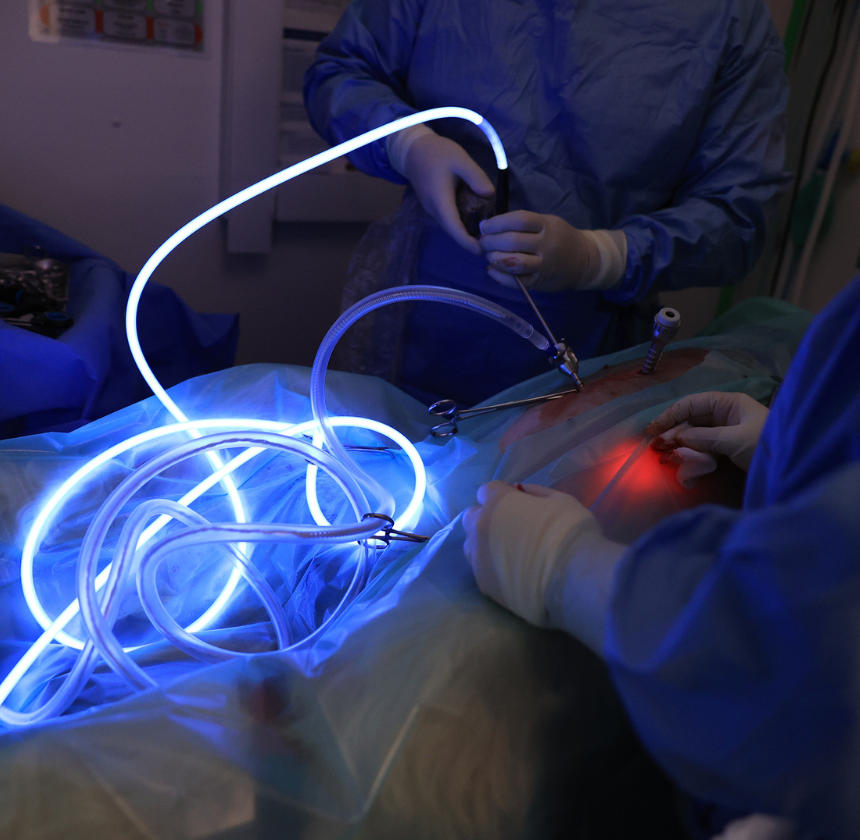
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
Providing advanced diagnostic solutions with minimal invasion.
What Is A Diagnostic Laparoscopy?
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the abdominal cavity in pets. It allows veterinarians to visually assess organs and tissues, aiding in the diagnosis of various internal conditions. This technique involves making small incisions and using a camera (laparoscope) to provide a detailed view of the abdominal area, enabling precise and accurate diagnoses without the need for larger, more invasive surgery.
When is Diagnostic Laparoscopy Recommended?
Diagnostic laparoscopy may be recommended for pets experiencing unexplained symptoms such as:
Chronic Abdominal Pain
Vomiting or Diarrhoea
Unexpected Weight Loss
Suspected Organ Abnormalities
Suspicious Growth or Mass
Bowel Obstruction / Foreign Body Investigation
Diagnostic Laparoscopy Procedure:
Diagnostic laparoscopy procedures involve several key steps, each designed to safely and effectively examine the abdominal cavity, providing a detailed view of internal organs while minimising tissue trauma and postoperative discomfort for the animal. Here’s an overview of the procedure:
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the procedure, your pet will undergo a thorough examination, including blood work and imaging studies (like X-rays or ultrasound) to assess their condition. These preliminary tests help guide the decision to perform laparoscopy and ensure that your pet is fit for anesthesia.
Anaesthesia and Sedation
General anesthesia is administered to ensure your pet is comfortable and completely relaxed during the procedure. This is necessary as the procedure involves examining internal organs.
Surgical Incisions
A small incision (or sometimes two) is made in the abdomen. Through these incisions, the laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) is inserted to provide a magnified, clear view of the abdominal cavity.
Visualisation
Using the laparoscope, the surgeon carefully examines the abdominal organs, looking for any signs of disease, injury, or abnormalities. The camera provides high-definition images that allow the veterinarian to identify issues that might not be visible through other imaging methods.
Diagnostic Findings and Sampling
If abnormalities are found, biopsies or tissue samples may be taken for further testing. In some cases, additional diagnostic procedures such as cytology or culture may be performed immediately.
Closure & Recovery
Once the examination is complete, the small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue. Most pets experience a quick recovery and may go home the same day or the following day, depending on the procedure’s complexity.
Diagnostic Laparoscopy Benefits in Pets
Overall, diagnostic laparoscopy offers numerous benefits for your furry friends, including accurate internal diagnosis, reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery, and a less invasive approach to exploring and treating internal health issues.
Minimally Invasive
Small incisions result in less pain, reduced scarring, and a quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Accurate Diagnosis
Allows direct visualisation of the internal organs, providing valuable information to diagnose conditions like tumours, infections, or structural abnormalities.
Reduced Risk
The procedure minimises the risks of infection, bleeding, and other complications associated with larger surgical interventions
Targeted Sampling
Enables precise collection of tissue samples (biopsies) for further analysis without the need for exploratory surgery.
Faster Recovery
Due to the minimally invasive approach, pets typically heal faster and return to normal activities sooner.
Improved Outcomes
Provides detailed insights into internal health issues, helping to guide the most appropriate treatment plan.